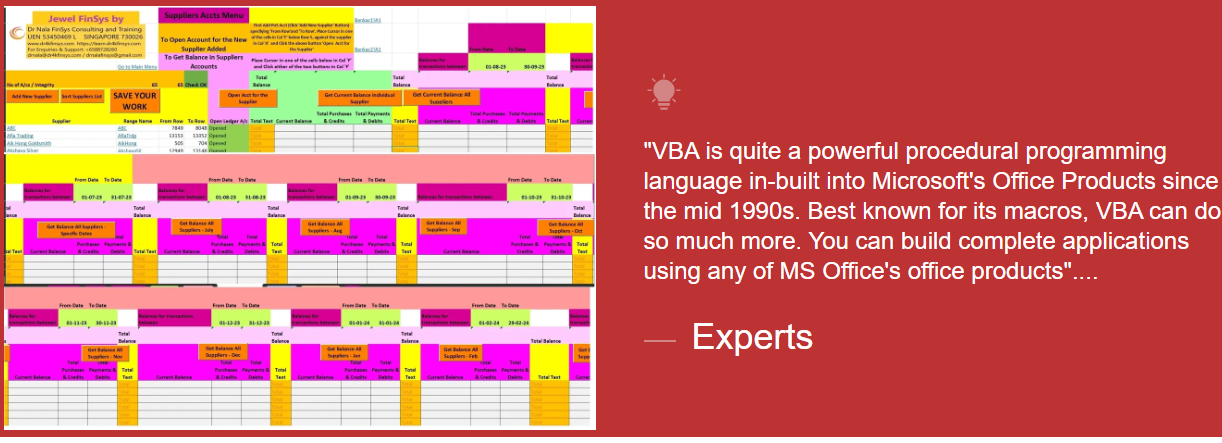
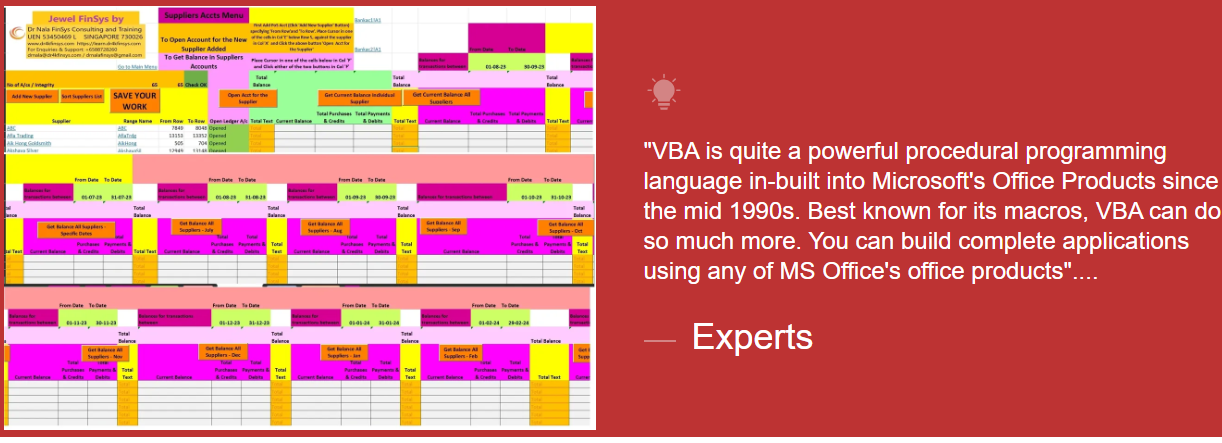
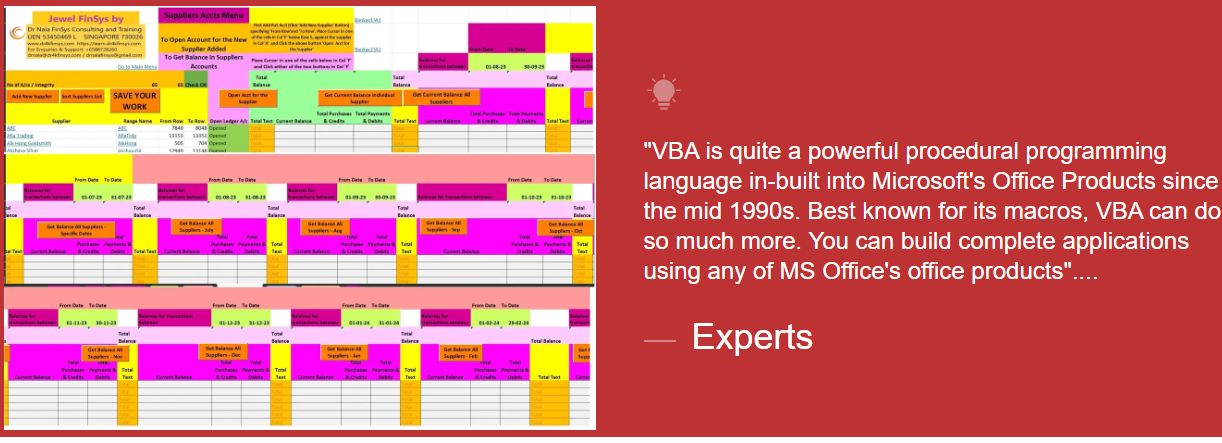
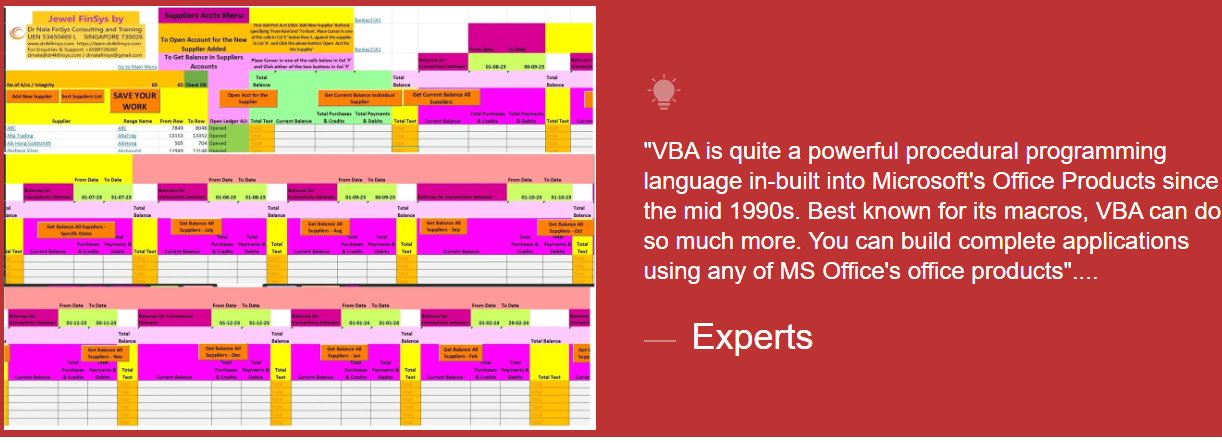
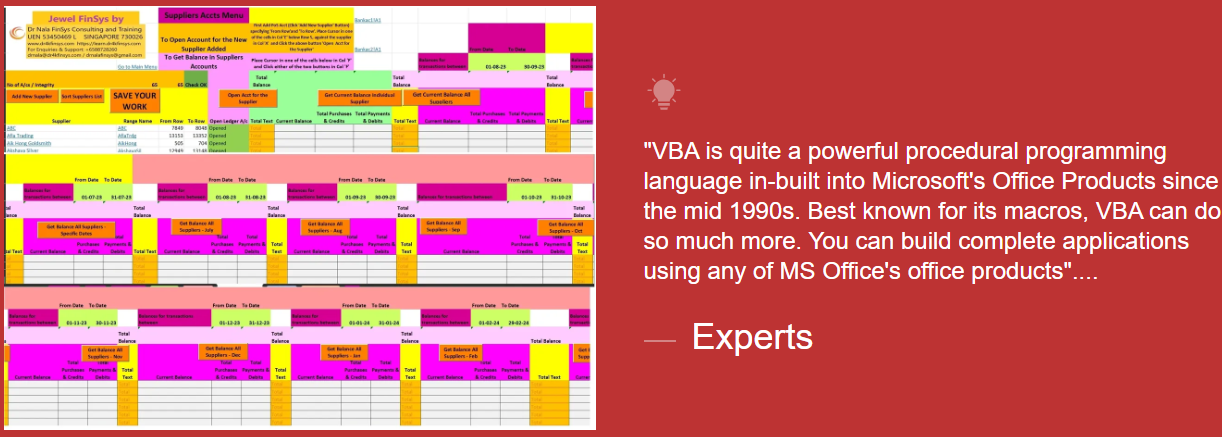
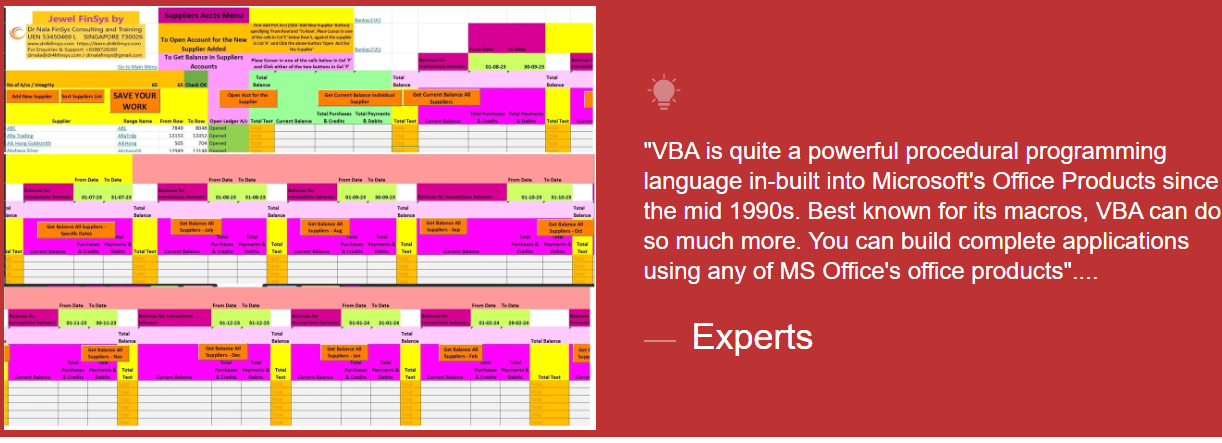
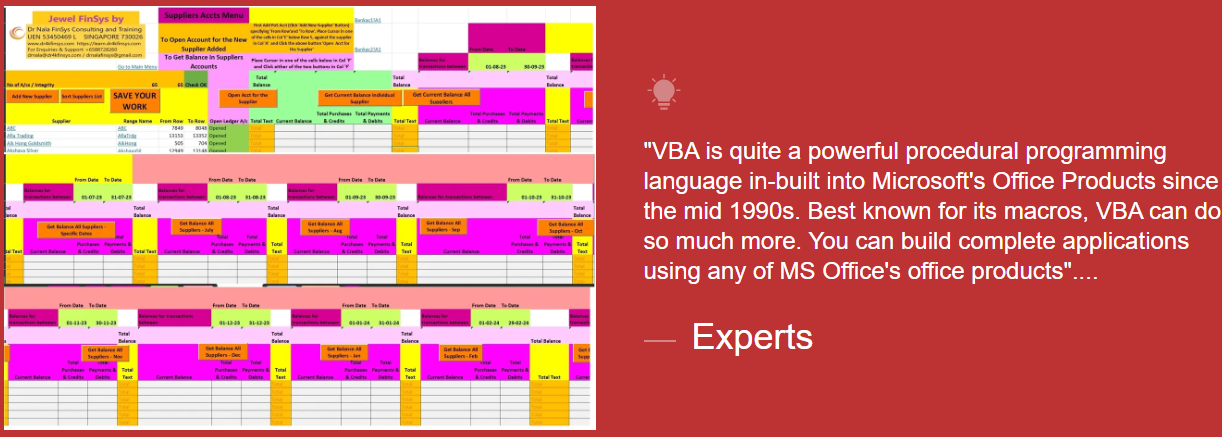
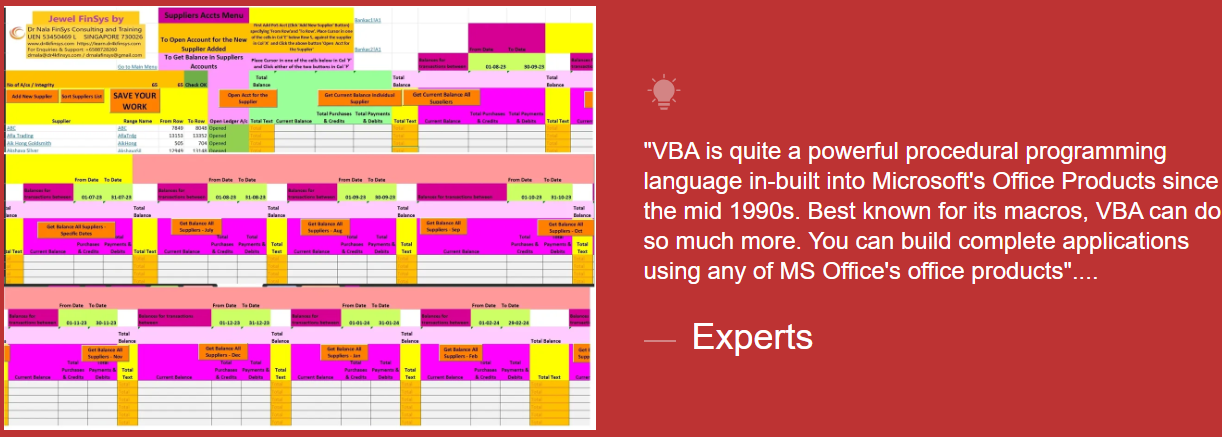
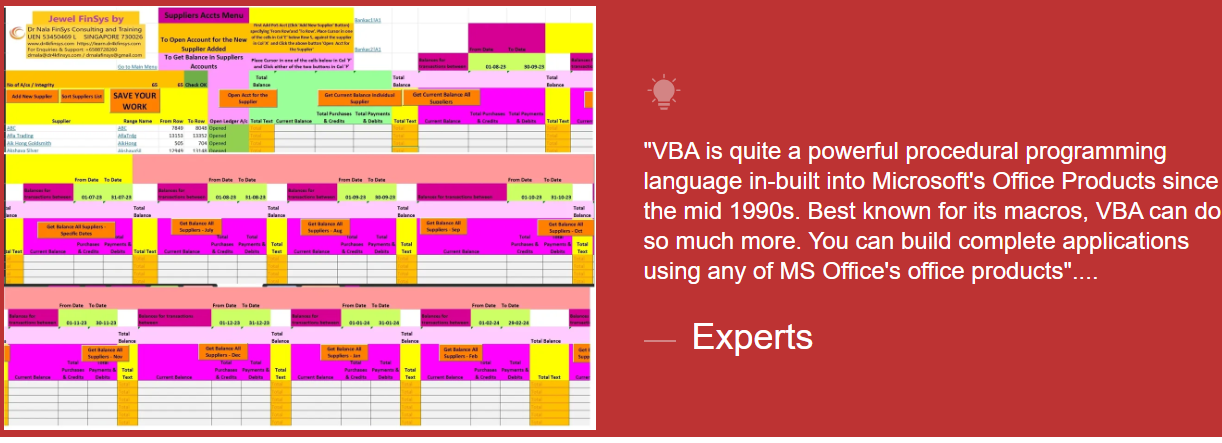
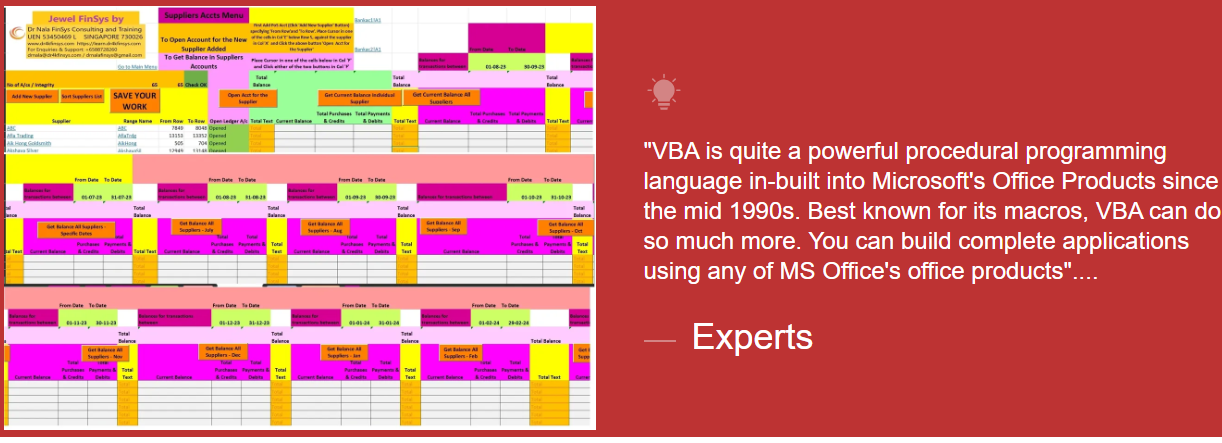
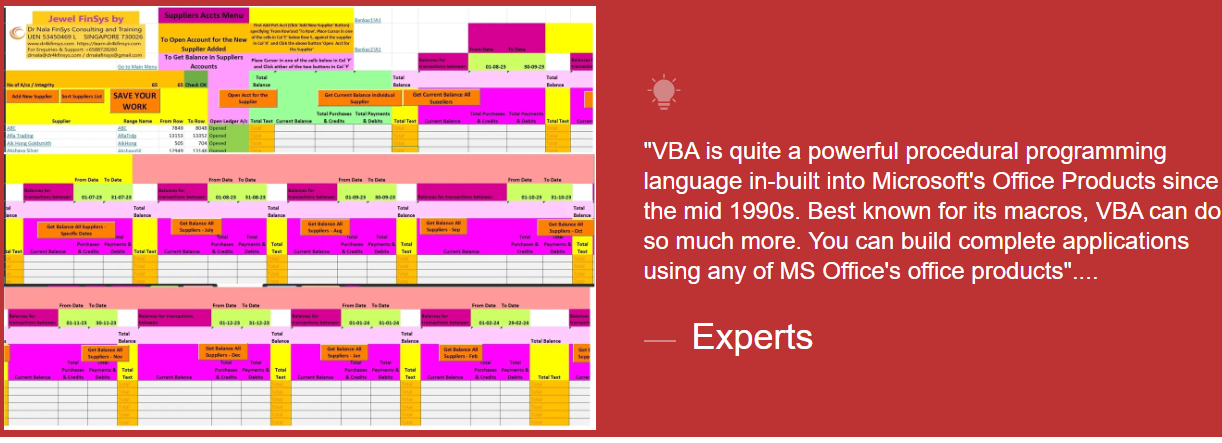
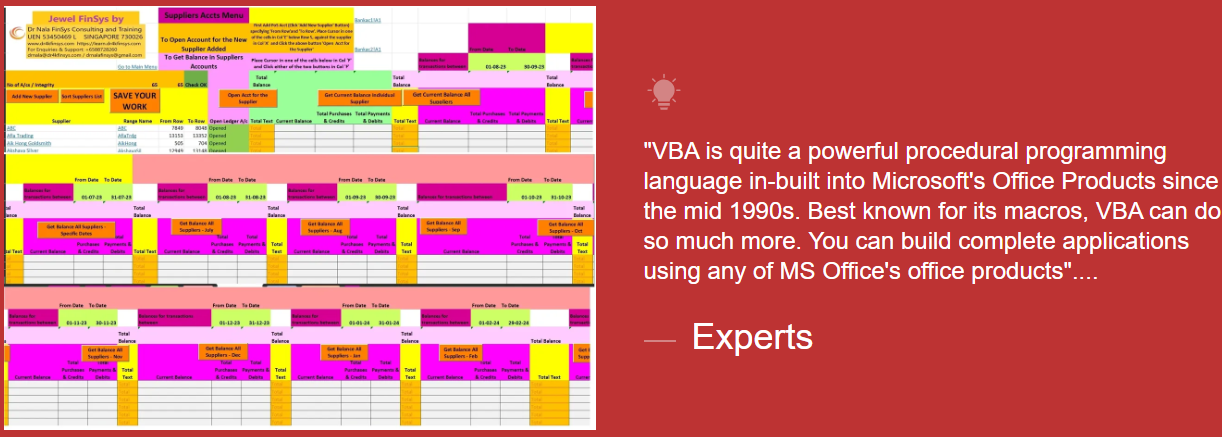
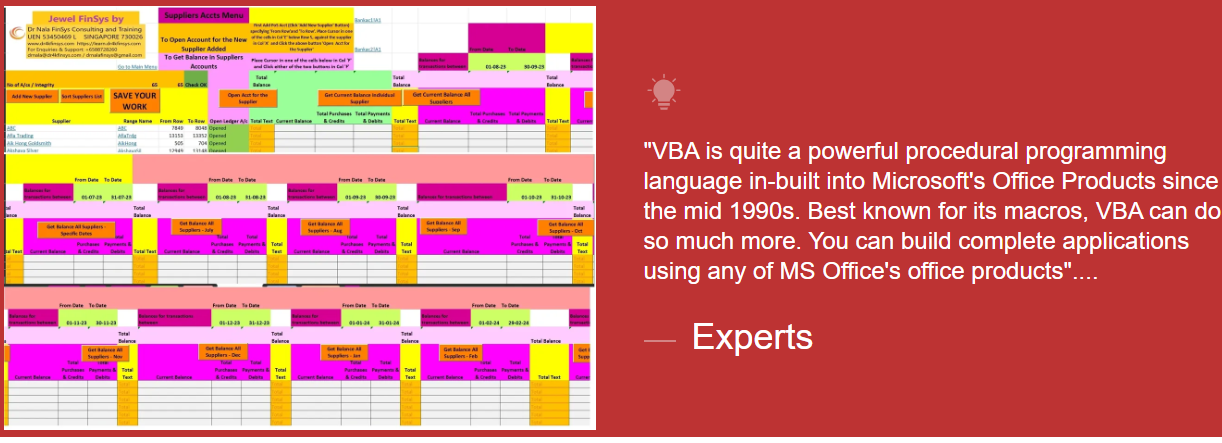
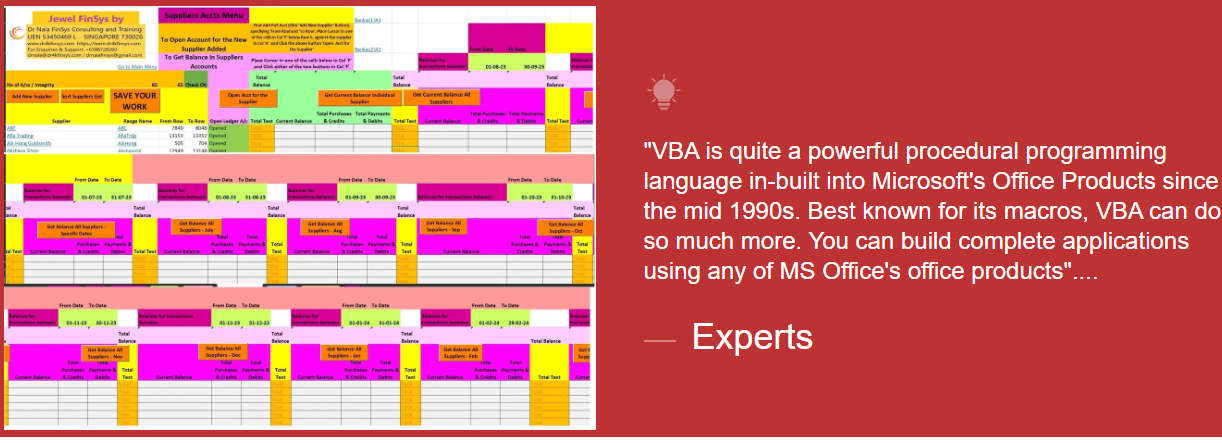
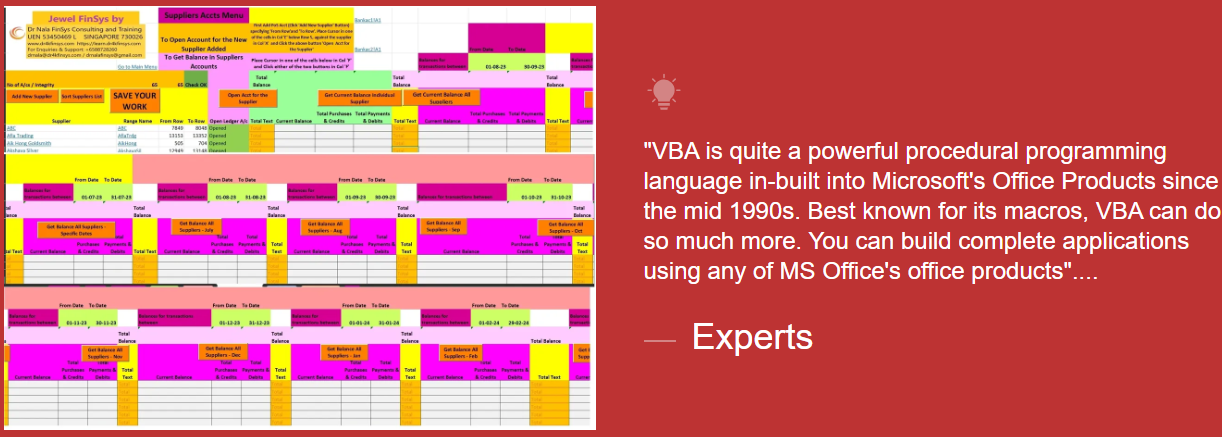
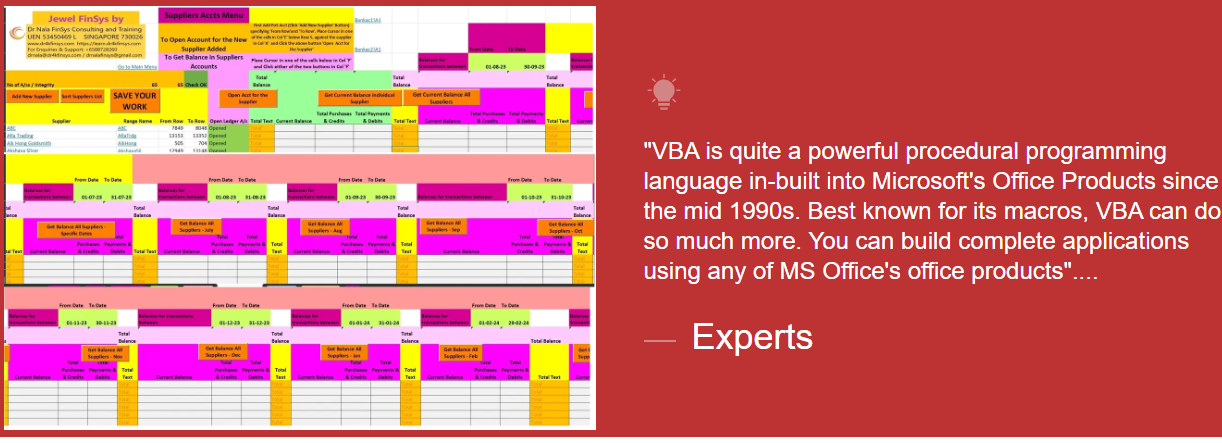
Module Aim
This course is designed to provide candidates with an overview of the presentation and disclosures of financial statements and an advanced knowledge of selected important accounting standards.
Syllabus Learning Outcomes
Candidates will be able to:
Understand the framework for the preparation and presentation of financial statements and the disclosure issues.
Identify the basic and further issues in the preparation of consolidated financial statements. Understand the basic concepts of deferred tax accounting, the disclosures and presentation issues.
Understand the concepts relating to foreign currency transactions and translation.
Account for financial instruments.
Understand emerging or other accounting issue
Module outline and detailed syllabus
1. Overview of Financial Statements
Framework for the preparation and presentation of financial statements
Objective of financial statements
Qualitative characteristics of financial statements
Recognition and measurement of the elements of financial statements
Concepts of capital and capital maintenance
Financial statements
Statement of Financial Position
Statement of Comprehensive Income
Concept of comprehensive income
Income Statement
Statement of Cash Flows
Statement of Changes in Equity
Notes to accounts
Other disclosure issues in the financial statements
Changes in accounting policy and estimates and correction of errors
Events after the balance sheet date
Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets
Operating segments
Related party disclosures
Earnings per share
2. Consolidated Financial Statements
Basic issues in the preparation of consolidated balance sheet and consolidated income statement
The acquisition method Goodwill on consolidation
Fair value adjustments
Non-controlling interests
Inter-company transactions and unrealised gains/losses
Further issues in the preparation of consolidated balance sheet and consolidated income statement
Investments in associates and equity accounting
Loss of control
Re-measurement of previously-held interests on acquisition date
Reverse take-overs
Complex group structure (e.g. father-son-grandson structure)
Interests in joint-ventures
3. Accounting for Income Taxes
Basic concepts in deferred tax accounting
Rationale for deferred tax accounting
Concept of tax base and temporary differences
Taxable and deductible temporary differences
Recognition of deferred tax assets/liabilities
Accounting for temporary differences
Recognized assets and liabilities in separate financial statements
Revaluation of recognized assets and liabilities in separate financial statements
Initial recognition of assets and liabilities in separate financial statements
Fair value adjustments recognized under the acquisition method in consolidated financial statements
Goodwill
Investment in subsidiaries and associates
Accounting for deferred tax assets
Accounting for tax losses
Deductible temporary differences
Measurement issues
Measurement of deferred tax assets/liabilities
Measurement of tax expense
Presentation issues
Presentation of current tax payable
Presentation of deferred tax assets/liabilities
Presentation of tax expense
Disclosure requirements
Reconciliation of effective tax rate/amount to statutory tax rate/amount
Analysis of temporary differences
Other disclosures
4. Foreign Currency Transaction and Translation
Foreign currency transactions and balances
Concepts relating to functional currency and presentation currency
Translation of foreign currency transactions and balances into an entity’s functional currency
Monetary items versus non-monetary items
Treatment of exchange gains/losses
Foreign operations
Re-measurement of foreign currency financial statements to the functional currency
Translation of financial statements prepared in an entity’s functional currency to a different presentation currency
Translation of foreign currency financial statements of subsidiaries and associates to the presentation currency of the parent
Translation gains and losses arising from translation of the separate financial statements of a subsidiary or an associate
Translation gains and losses arising from the translation of goodwill and fair value adjustments
Allocation of translation gains and losses to non-controlling interests
5. Accounting for Financial Instruments
Theoretical and practical considerations underlying the application of FRS 32, FRS 39 and FRS 107
Recognition and derecognition
Recognition of financial assets: primary instruments and derivative instruments, stand-alone and embedded derivatives
Recognition of financial liabilities
Derecognition of financial assets and liabilities
Measurement
Measurement of financial assets: “fair value through profit or loss”, “available-for-sale”, “held-to-maturity”, and “loans and receivables”
Measurement of financial liabilities
Presentation
Substance over form
Split accounting for compound instruments
Off-setting of financial assets and financial liabilities
Disclosure
Risk management policy
Fair values
Other disclosures
Hedge accounting
Fair value hedge
Cash flow hedge
Hedge of investment in foreign entity
6. Emerging or Other Accounting Issues
This topic deals with conceptual and qualitative issues relating to:
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments
Compensation-related issues including accounting for share-based compensation
Issues addressed in exposure drafts (ED/FRS and ED/INT FRS) that have significant impact on future accounting practices
Contentious or evolving issues relating to Topics 1- 5 of this syllabus